How to Choose a Gas Chromatographic Detector for my Analysis?
In Gas Chromatography detection is based on a property of the eluting compound which is different from the carrier gas. It is necessary to have a clear understanding of your analysis requirements in advance before you can decide on the suitability of the detector. Important considerations are:
- Is the detector Destructive or Nondestructive. Nondestructive detectors are concentration sensitive and can be used in series before destructive detectors. On the other hand destructive detectors are mass sensing and cannot be used in conjunction with other detectors.
- Sensitivity requirements in terms of lowest detectable quantity and large linear dynamic range.
- Selectivity refers to what type of compounds a detector will respond to falls into two categories
- Universal detectors respond to all compounds reaching them from the column
- Selective or specific detectors respond only to a class of compounds containing a particular functional group (selective) or only to a particular compound (specific)
Once you have the clarity on the requirements of your analysis the next stage is selection of your Gas Chromatographic detector from the available options.
We shall consider some common detection options available:
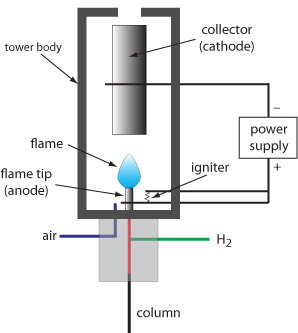
Flame Ionization detector
Flame ionization detector is the most commonly used detector as it responds to most organic compounds that can ionize in the hydrogen – air flame. It has a vast linear dynamic range of \(10^ 7\).
It is not suitable for inorganic gases such as CO, \(O_2\), \(CS_2\), \(N_2\), \(CO_2\), \(H_2O\) and \(NO_x\) and inert gases.
Thermal Conductivity detector
Thermal Conductivity detector is nondestructive and universal. It responds to compounds which have thermal conductivites different from the carrier gas. Inorganic gases which cannot be detected on FID can be analysed with the TCD. Its linear dynamic range is \(10^6\). It has useful applications in analysis of natural and refinery gases.
Electron capture detector
Electron detector is nondestructive and selective to compounds with electro negative substituents such as halogens, nitriles, nitrates, conjugated carbonyls, organometallics and oxygenated components. Linearity is \(10^5\) and applications include chlorinated pesticides, polyfluorinated biphenyls and herbicides.
Nitrogen phosphorus detector
Nitrogen phosphorus detector responds selectively to most compounds that contain nitrogen or phosphorus. Linear dynamic range is \(10^6\). Widely used for drugs of abuse and pesticides containing nitrogen or phosphorus.
Flame Photometric detector
Flame Photometric Gas Chromatographicdetector is destructive and selective. It is sensitive to compounds containing phosphorus or sulphur. Linear dynamic ranges from \(10^3\) for S to \(10^4\) for P. It is useful for analysis of organophosphorus pesticides, sulphurf in petroleum products and pulp milling process studies.
Photo Ionization detector
Photo Ionization Gas Chromatographic detector is a nondestructive and selective detector. It responds to compounds ionized by UV light such as aromatic and unsaturated compounds in drinking water, wastewater and sludge. Benzene, toluene, xylene and PAH’s in petroleum products. Linear dynamic range is \(10^7\).
Electrolytic Conductivity detector or Hall detector
Electro Conductive the Gas Chromatographic detector is sensitive to halogens, sulphur and nitrogen compounds, PCB’s, volatile organic compounds, sulphur compounds such as petroleum products and pesticides. Linear dynamic range is \(10^6\) for chlorine.
Mass Selective detectors
These Gas Chromatographic detectors are destructive and are based on the fragmentation of molecules by electron bombardment and separation based on mass to charge ratio. Linear dynamic range is \(10^5\). Applications include pharmaceuticals, environmental monitoring and pesticide residue analysis.
Please do leave your comments on analysis using such Gas Chromatographic detectors.


Responses