Analytical Method Validation
The analytical results you communicate can have far-reaching consequences and can form the basis for taking decision on safety of use of commercial products, foods and natural resources in addition to decisions involving legal matters.
As a responsible analyst before you undertake analysis in the laboratory you should make sure that your results are authentic and are universally acceptable. This key objective can be realized only if the method selected for the purpose is duly validated.
Analytical method validation establishes documented evidence that the procedure adopted for a test is fit for the intended purpose in terms of quality, reliability and consistency of results.
What Is Analytical Method Validation?
Analytical method validation establishes documented evidence that the procedure adopted for a test is fit for the intended purpose in terms of quality, reliability and consistency of results.
In other words, if the same method is adopted in any other laboratory across the world, under the same set of conditions and control parameters, the results should be in agreement.
Each and every method requires validation:
- Before putting to routine use
- When analytical conditions are changed such as change of technique, change in desired concentration range or change of sample matrix
- Whenever changes are made to an existing procedure
It is important to collect relevant information on analysis requirements before you plan validation of the procedure
- Components to be detected
- Expected concentration levels
- Required level of detection and quantification
- Nature of sample matrix
- Type of analytical technique to be used
- Required degree of precision and accuracy
Parameters of Method Validation
Before undertaking the method validation procedure, it should be ascertained using reference standards that the response of the analytical measurement is on account of the analyte of interest and not due to any other chemical species.
After this has been established, you may proceed with the validation which evaluates the following method-specific features. Here are the various method validation parameters.
- Selectivity and specificity
- Linearity
- Range
- Accuracy
- Precision
- Limit of quantification
- Ruggedness
- Robustness
We shall discuss each of the analytical method validation parameters in detail so that you can better understand analytical method validation.
Selectivity and Specificity
Selectivity and specificity are often used synonymously but these are different terms. Specificity is the unequivocal response of the technique to a specific analyte present in the sample whereas selectivity can be applicable to a collective response to a group of analytes having similar chemical and physical characteristics.
The method selected should meet the criteria for selectivity and sensitivity in presence of deliberately added interferents that can be expected in the sample under investigation.
Selectivity is more frequently used as analytical techniques and is seldom specific to only one analyte. Further, selectivity should not be affected by interfering species such as degradation products, impurities and other matrix components.
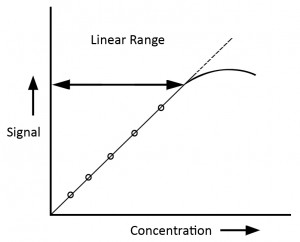
Linearity
Linearity refers to the ability of analytical procedures to produce results in direct proportion to the concentration range of analyte in samples within the required concentration levels.
- Linearity should be determined using a minimum of 6 standards whose concentration spans from 80% to 120% of expected concentration level.
- Linearity report should include slope of line, linear range and correlation coefficient data. Correlation coefficient r should be greater than or equal to 0.99 in the working range
Range
Operating range is deduced from the calibration plot. It is the interval between the upper and lower concentration of analyte falling in the linear range. The results corresponding to this range demonstrate acceptable levels of precision, accuracy and linearity.
Accuracy
- Degree to which the determine value of analyte corresponds to the true value.
- Accuracy can vary over the expected concentration range.
- It should be determined using a working or reference standards in the 80% – 120% level of expected range
- Accuracy is determined by :
- Analyzing a sample of known concentration and comparing with the true value
- Spiking a blank (Sample having all components except the analyte) and comparing with the expected result.
- Standard addition method in which the sample concentration is determined. A known amount of analyte is added and the concentration is once again determined. The difference of the two concentration values is compared with the actual value of added analyte.
- Accuracy is also defined by the comparison of test results with those obtained using another validated test procedure
Precision
- Precision expresses closeness of a series of measurements of the same sample under identical conditions
- High degree of precision does not necessarily means a high degree of accuracy
- Precision is expressed as variance, standard deviation or as coefficient of variation of a series of measurements
- Minimum of five replicate sample determinations should be carried out
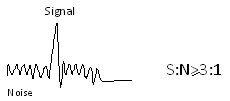
Limit of Detection
- Lowest amount of an analyte that can be detected but not necessarily quantified
- Lowest concentration of calibration standard which produces a peak response corresponding to the analyte should be measured at least 6 to 10 times. Average response (X) and standard deviation (SD) are required to calculate limit of detection
Limit of detection = X + (3SD)
- Signal to noise ratio at limit of detection should be at least 3:1

Limit of Quantitation
- Lowest amount of the analyte that can be quantitatively determined with defined precision under the stated experimental conditions
- 6 – 10 observations should be made for average response and standard deviation
Limit of quantitation = X + (10SD)
- Signal to noise ratio should be at least 10:1 at the limit of quantitation
Ruggedness
Ruggedness measures reproducibility of test results under following conditions :
- Results generated for same sample under identical conditions by different laboratories
- Results generated for sample under identical conditions by different analysts
- Same analysis using different instruments
- Same analysis under different environmental conditions
- Same analysis using test materials from different sources
Robustness
Robustness examines the effect of operational parameters changes on the analytical results
- pH
- Temperature
- Operational conditions such as flow rate, injection volume, detection wavelength or mobile phase composition in chromatographic analysis
Variation should be deliberate but within realistic range to study the robustness of the method. The results of the analysis after making the deliberate changes should be within the method’s specified tolerance limits.
Method validation may appear to be a tedious and time-consuming activity but once the method is validated before adoption, it will not let you down under any circumstances.
What Is the Need for Analytical Method Validation?
Before you plan an analysis of a sample in your laboratory, you should be aware of the essential details of the sample like its homogeneity, physical state, available quantity and stability.
It is also essential to know the requirements of analysis such as:
- Components to be detected and quantified
- Expected concentration levels
- Nature of the sample matrix. In other words, the nature of interferences that can be present that can complicate the determination of required components
- Required degree of accuracy and precision
- Appropriate analytical technique for the analysis
- Material and apparatus required for the analysis
- Availability of required resources
- Cost of analysis
The above considerations require a judicious selection of the method. Let us see what could be those useful reference sources that you can access. You can consider yourself fortunate if your laboratory has already a validated method available which can be adopted without applying a second thought. However, this may not be the case every time, and you would feel the need to search for a suitable method due to the following constraints:
- The sample matrix is different from routine samples and requires a different set of extraction procedures or can introduce different interferences
- Non-availability of required reagents or glassware
- Non-functional or un-calibrated instruments
In such situations, you will have to look for other alternative methods so you will have to search for the method through the available options such as:
- Standard textbooks
- Reference analytical journals
- Pub Med
- Google search
The more you search, chances are that you may get confused further. Let us assume that after going through the references you have zeroed down on a particular method.
Now comes the important stage of validating the method before it is put into routine use. You have to keep in mind the fact that the analytical results reported by you can have far-reaching consequences concerning the safety of use of the products, efficacy of drugs, toxic limits for environmental samples, or verdict on legal matters.
As a responsible analyst, you have to make sure that the data reported by you is reliable and would be accepted universally. Such objectives can be achieved only by following the rigorous validation process.
Validation becomes necessary:
- Before adopting the method in routine use
- Whenever there is a requirement of analysis of components in the different sample matrix
- Sample analysis requires different analytical procedures
As a regular practice, any method needs to be validated before adoption. However, it would need to be revalidated under the following situations:
- Any changes made in the established procedure
- Any new accessory is added to the existing system
- The system has undergone major operational problems which have been rectified.
Why Is It Essential to Adopt Validated Analysis Methods?
Analytical chemistry is a science which guides you on how to get the desired information from your sample. The method validation guidelines provided comprise of
- Selection of appropriate technique
- Procedure to be followed
- Analysis and Interpretation of data
- Environmental controls and other precautions to be adopted
You can consider yourself lucky if a validated method meeting your analysis requirements is already available in your laboratory. Alternately, you will have to identify the appropriate method through a literature search.
Your literature search will be successful if you have clarity on your analysis objectives. The search can be initiated using Internet search engines or referring to documented sources such as research journals. The next step is to validate the method before adopting it.
Benefits of Method Validation
Method validation is a practice which can prove to be beneficial in a number of situations such as:
- Publication of your findings in international journals of repute or presentation in professional conferences
- Instils a degree of self-esteem and confidence in yourself as well as in those who use your results
- Acceptance of procedures and results by accreditation bodies and external auditors
- Arriving at critical decisions concerning the use of data with regards to the safe use of products by consumers
- Freedom from disputes concerning non-agreement of test results with other laboratories
Critical Role of Method Validation in Chemical Analysis
Each and every analysis requires the choice of a method that will help you achieve the required objectives. In case an established method is available, you should consider yourself fortunate as this will save you the effort and time required to validate the method before adopting it.
Several options are available to you for the selection of the method to suit your analysis requirements. Such options include a survey of standard analytical textbooks, research journal publications, Google search, etc.
You will come across several methods in your Google search but this can add to further confusion as the method selected may not be suitable for your analysis requirements.
In making your method choice, you also have to keep into consideration other factors such as:
- Cost of analysis
- Availability of required reagents and standards
- Availability of required instrumental facilities
- Availability of trained manpower
- Time requirement for analysis
- Simplicity of method
It is essential to keep in mind that the simplest method may not be the ideal one so you have to carefully evaluate the choice keeping in view the considerations listed above.
Now that you have been introduced to analytical method validation, please feel free to ask any questions you have in the comments below.





Do you have a similar summary for manufacturing a diagnostic based on biologic material ? (ie, process validation of immunoassays intended as IVDs?).
Thanks!
Susanne
Hi Susanne, we don’t have such a summary ready but we will consider it for the future and keep you posted if we do make it.
Please let me know acceptance criteria of Accuracy and Precision determinations.
Thanks
Hi Vishwanath, the acceptance criteria have to be based on the application of your method. USP and other guidelines clearly state that you have to establish these based on what you will use the method for. You can refer to the IUPAC guidelines for a table which summarizes the criteria for different ranges of measurement and if you share your exact requirement I might be able to dig it out for you.
Please let me know the acceptable range for change in pH, tempearture etc for robustness.
Thanks
Swati
Dear,
pH always ± 0.05 to the target and the robustness purpose we can study upto ± 0.1 in the validation. The temperature is based on the instrument temperature calibration limit. With in the range we need to the robustness test and shall be validated.
Thanks and Regards
Dharmakkannu
Please, what can can increase in BOD and COD of an effluent treatment plant of a paint industry.
Thanks
Hi Ojo, For this you will need to reffer the law and the requirements in your country.
I want to learn step by step procedure of analytical method validation and calculation
Dear Dharmendra,
The topic is briefly covered in the certificate programmes but we do have plans to provide an elaborate treatment through a dedicated programme on the topic which we shall roll out sometime in future.
Kindly help me on the application or use of HPLC in various fields/ industries (eg mining, agriculture, pharmacitical etc ) where analytical chemistry is applied. please
Hello Malgas,
I would recommend our Certificate Course on HPLC to you as it would meet your requirements. It is an online programme and you would be able to complete it as per your convenience.On completion you would be eligible for our certificate as well.Please go to the site for joining details.
Which concentration can be used for HPLC method validation of drug product either label claim or COA?
Hi, the concentrations are used based on the claim.
Great introduction to analytical method validation! I’m looking forward to reading more.