Comparison between Electrode-less Discharge Lamps and Hollow Cathode Lamps as light sources in AAS
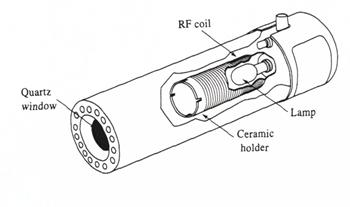
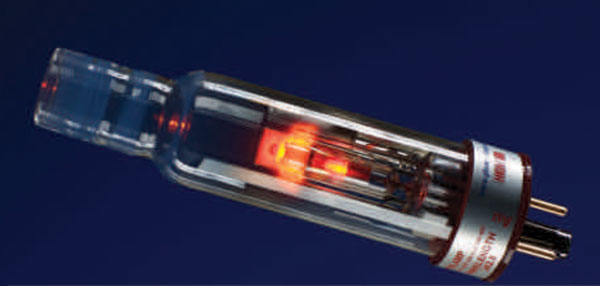
Electrode – less discharge lamps provide high intensity (!0-100 times) and narrow emission lines which lead to higher signal – to -noise ratios over the lines obtained using hollow cathode lamps.

Our earlier article Types of light sources in Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy covered the essential features of the two commonly used light sources – hollow cathode camps and electrode – less discharge lamps. The benefits of electrode- less discharge lamps are realized especially when analysing volatile elements like As, Sb, Bi, Cd, Hg, Rb, Sn, Te, etc. Sputtering of such metal atoms and their adsorption on cathode lamp side walls and windows begins to affect the useful life of the lamps. On the other hand electrode – less discharge lamps because of the high emission intensities overcome the problem easily and provide lower detection limits.
Electrode – less discharge lamps are further subdivided into two categories – microwave and radio frequency excited lamps.
Microwave Electrode – less discharge lamps
Microwave lamps are excited by microwaves generated at frequencies around 100 MHz. The intensity of microwave lamps is better than radiofrequency lamps. Seeding with (1-2mg) mercury leads to mercury vapour preventing adsorption of metal onto the walls and windows of the lamp thereby increasing its useful life. However, microwave discharge lamps require temperature regulation to give a stable line intensity.
Radiofrequency Electrode – less discharge lamps
The intensities of radio frequency electrode- less discharge lamps are generally lower in comparison to microwave lamps.
Radiofrequency electrode – less discharge lamps operate at optimum level of 27.12 MHz and give better stability than their microwave equivalents though intensities are somewhat less. Such lamps do not require temperature stabilization.
Electrode- less discharge lamps with all their benefits are not as popular as hollow cathode lamps and are used mainly for analysis of about 15 volatile elements. The reasons are mainly higher cost and difficulty in operation in comparison to hollow cathode lamps.
Please share your experiences on lamp usage and offer your valued comments.



Responses