What are essential considerations for disposal of Laboratory Waste?
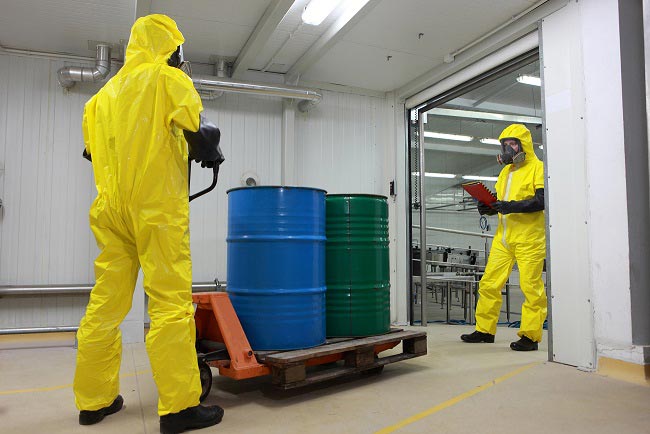


Laboratories constitute a major source of contamination and pollution of water drainage systems and environment. Atmospheric environment pollution is fairly less in comparison to contamination of drainage systems.
As a responsible citizen you should follow the prescribed norms so that there is minimum contamination or harm to others.
The subject has gained importance and guidelines have been prescribed by different institutes and universities for their internal guidance to constituent laboratories. The objective of this article is to briefly summarize the important considerations that should be taken in disposal of different categories of laboratory wastes.
Chemical Laboratories
- Chemical laboratories constitute the largest number if you bracket together academic, industrial and commercial testing laboratories.
- Harmless soluble inorganic salts and weak acids or alkalis can be disposed down the drain with excess of water
- Compounds of highly toxic elements, organic solvents, organohalides, pesticides, mercury, poisonous cyanides, metallic phosphides and fluorides should never be disposed down the drain. Such waste should be disposed in special bins for separate treatment prior to disposal
- Organic waste should never be mixed with aqueous wastes and collected separately. Such types of containers should be properly labeled.
- Broken glass, needles, tubes, blades, etc should be stored in thick plastic bins. Always leave some space and do not overfill the bins to permit safe handling. Contaminated glass should not be sent for recycling. Such containers should be properly labeled for preventing injury to disposal staff
- Empty winchesters and bottles can be reused for same acids or solvents. If required to be used for disposal of waste solvents they can be washed prior to use.
- Corrosive liquid containers should bear list of solvents added. Corrosive waste should be stored in non-metallic containers
- Liquid waste containers should be leak free and secured with screw top caps
- Peroxides have a tendency to form crystalline deposits which on drying can detonate due to pressure sensitivity. Such wastes need careful handling to avoid mechanical impact of containers during handling
- Organic solvents, soluble organic waste and halogenated organic compounds should be sent for incineration.
Life Science Laboratories
Waste from life science laboratories present biohazards in addition to chemical hazards.
Earlier article on Spill Management covered handling of spills in different laboratories.
- Autoclave the laboratory waste and samples before disposal
- Use separate bins for disposal of needles and sharps. Before disposal autoclave all contaminated objects
Finally as a responsible scientist you should not try to hide any waste resulting from accidents or conceal facts because this can result in bigger hazards to unsuspecting workers of the laboratory.
Please do offer your views and comments on the article.




Responses