Advantages and Disadvantages of different HPLC Pump Configurations
A brief introduction to different types of HPLC pumps was provided in module 7 of our free course on HPLC. A HPLC pump should be able to deliver constant flow of mobile phase which is pulse free and independent of column back pressure fluctuations.
Modern HPLC systems are based on reciprocating pump designs. In the present article the advantages and disadvantages of such HPLC pump designs are discussed.
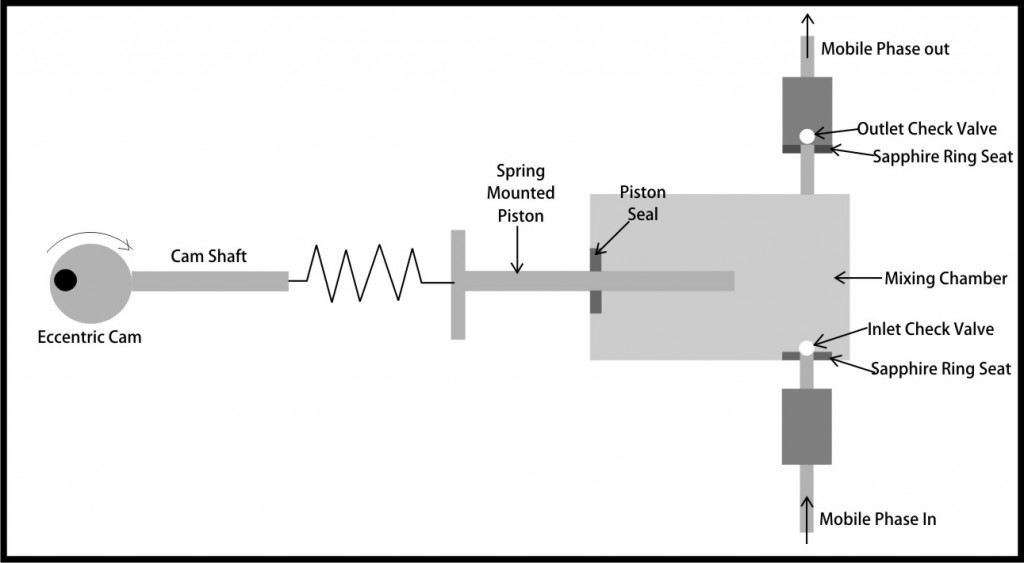
Electric motor driven eccentric cam drives the spring mounted piston in and out inside the mobile phase mixing chamber. In the rear position the mobile phase gets sucked in due to lifting of the inlet check valve In the forward stroke the inlet check valve rests on the inlet thereby blocking backflow and the collected liquid is forced out through the outlet through lifting of the outlet check valve. The same process gets repeated with each piston cycle. The pumping rate can be adjusted by controlling the speed of cam rotation.
Advantage
- Simple design reduces maintenance costs.
Disadvantage
- Flow out of the chamber gets intermittently stopped during the fill cycle and this results in periodic pressure pulses which contribute to noisy baselines.
Dual Piston Reciprocating Pumps
Pressure pulses are easily overcome by using dual piston HPLC pumps which incorporate pump heads operating exactly 180° out of phase which results in uninterrupted delivery of mobile phase at constant pressure.
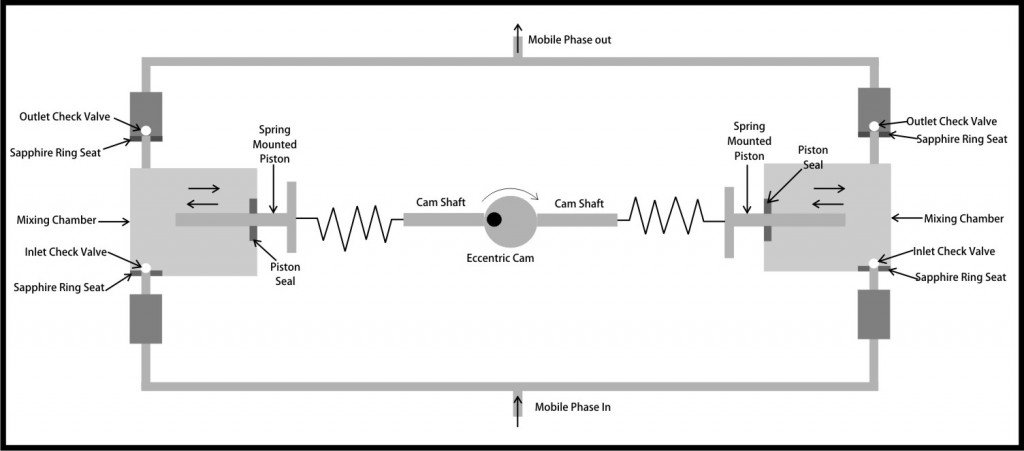
Two chambers are controlled by a single motor by a common eccentric cam. This common motor allows one piston to deliver while the other is refilling the other chamber and vice versa. As a result the pulsations get eliminated to a large extent.
Advantage
- Pressure pulse free delivery of mobile phase
Disadvantages
- More number of moving parts
- HPLC pump operation reliability depends on clenliness of mobile phase, sample and proper operation of all four check valves during each cycle.
- HPLC Pump failure can result from failure of check valves, pistons and piston seals.
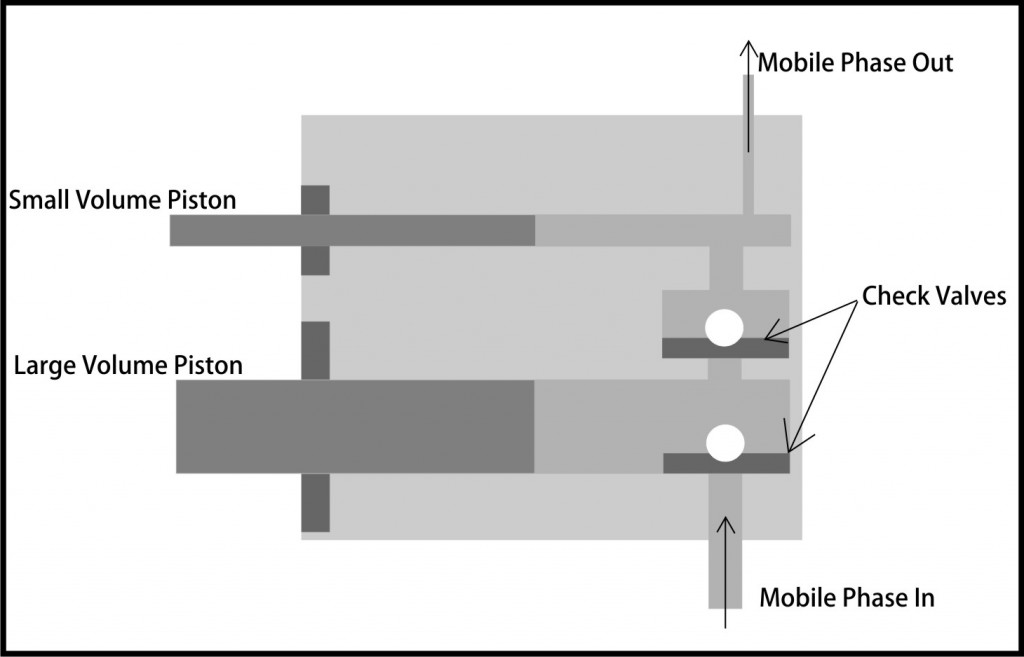
Both the small and large volume pistons operate 180° out of phase. The bigger piston is sucking the mobile phase while the smaller one is pushing it out. When the pistons change direction, the bigger piston simultaneously refills the smaller chamber and dispenses the eluent into the HPLC system.
Dual piston (different piston speeds) – 3 check valves
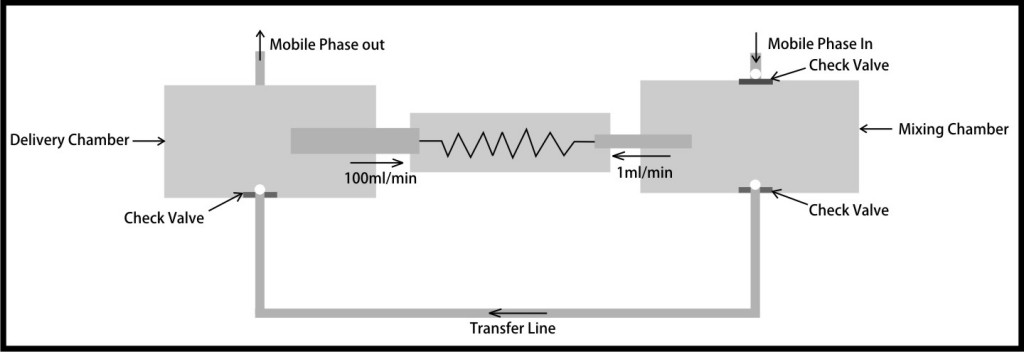
The arrangement is based on different speeds of same volume pistons. Suction of mobile phase in mixing chamber takes place at a low speed (around 1mL/ min) but transfer by delivery piston through transfer line takes place at a higher speed (say 100ml/min). This provides high efficiency of solvent mixing due to high turbulence inside the delivery chamber.
Advantages
- Elimination of cavitation and air bubbles inside the delivery chamber
- Reproducibility of flow rate because check wall arrangement prevents backflow during delivery stroke.
We have seen that the common objective of all HPLC manufacturers is to develop pumps that are capable of delivering mobile phase at a consistent flow rate without any pressure pulsations.
Hope you found the article informative. Kindly share your comments and experiences.



Very interesting points you have remarked, appreciate it for putting up. “Ignorance, the root and the stem of every evil.” by Plato.