Contribution of HPLC to Nutritional Labeling of Foods

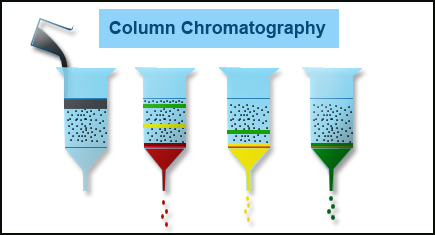
HPLC or High Performance Liquid Chromatography has a marked presence in modern analytical laboratories. The major applications cover basic research and industrial quality control particularly in studies on biomolecules, pharmaceutical manufacturing and new drug development, stability studies on foods and pharmaceuticals and clinical monitoring of body fluids.
The present article covers the contributions of HPLC in a relatively new area of application, namely, nutritional labeling. The awareness on nutritional potential of foods has spread over the years. In the year 1990 that Nutritional Labeling and Education act or NLEA stipulated that all processed foods should bear relevant information on their nutrient content levels. The act was adopted universally and several revisions evolved in different countries. In India the Packing and Labeling regulations were introduced in 2011 by Food Safety and Standards Authority of India or FSSAI. Under the provision of this regulation nutritional information should be mentioned on the product label. Any manufactured food product not bearing such a label or bearing incorrect information will be deemed to be misbranded or substandard and the manufacturer would be liable to be punished under the existing provisions of the regulation. Such regulations have resulted in stringent analysis requirements on all processed foods. The Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) International came out with methods for different categories of foods. National standard bodies have evolved their own food standards based on procedures laid down by the AOAC and other organizations such as American Oil Chemists Society (AOCS), American Association of Cereal Chemists (AACC). Chromatographic techniques constitute a majority of the proposed methods.
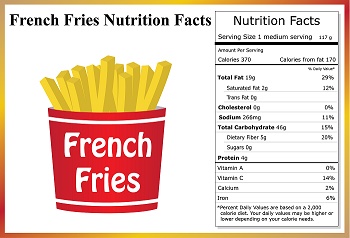
Nutritional parameters
The labels on food products commonly contain information on following nutritional parameters
- Vitamins
- Protein
- Energy
- Minerals
- Carbohydrates
- Dietary fibre
- Fats
- Cholesterol
Based on laboratory testing the label should comply with the printed values within specified limits. Excess can lead to medical side-effects such as nausea, cramps, liver damage, deformities or diarrhea.
Role of HPLC in nutritional labeling
HPLC technique provides high sensitivity and selectivity of the components present in complex food matrices. This feature makes it an ideal choice for nutrition labeling requirements of the following nutritional parameters:
Vitamins
Vitamins constitute a range of organic compounds which play a vital role in normal functioning of the human body. The body’s requirement of vitamins is in small doses so their analysis can offer a challenge to the analytical chemist. Vitamin analysis serves to ensure product quality and justify the claims on the labels.
Vitamins fall into two major groups. Fat-soluble group includes vitamin A, D, E and K which can dissolve in organic solvents. C – 18 columns provide a versatile separation for a range of fat-soluble vitamins. On the other hand water soluble vitamins cover both acidic and basic molecules which show polar characteristics and include vitamin C, B1, B2, B3, and folic acid. Usually the analysis of such polar components is carried out with ion pairing agents for improved retention times
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are common constituents of food and beverages.
They include simple sugars, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.Fructose,sucrose, maltose and lactose in addition to sweetness add texture to the foods. An oligosaccharide comprises of a polymeric chain having 2 – 10 simple sugars whereas a polysaccharide can have more than 10 simple sugars and can cover starches and gums.
HPLC analysis is commonly carried out using an amino-based column with isocratic mobile phase and a refractive index detector
Proteins
Proteins are polymeric materials having high molecular weights (>5000) whose building blocks are amino acids. Aqueous mobile phases using C – 18 columns in reverse phase mode and UV detector gives satisfactory separation of organic acids in beverages and fruit juices.
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a lipid found in tissue. It is essential for good health but there is an established correlation between high levels of cholesterol and cardiovascular problems. Low density lipoprotein cholesterol or LDL causes clogging in blood vessels and is considered to be bad cholesterol. On the other hand high density lipoprotein cholesterol is considered to be good cholesterol as it prevents heart disease by removing bad cholesterol from blood. HPLC determination yields reliable results on cholesterol levels in various food products such as eggs, meat, milk and other dairy products.
Energy
Energy of a food product is an essential detail that needs mention on the label as health conscious population is critical on calories intake. It is expressed in units of kcal/ gram or kjoules/ gram. The energy value is not obtained by direct determination using HPLC but can be determined from the values of carbohydrates, protein and fats by the formula
Energy= 4 X(carbohydrate + protein) +9 X fat
It can be seen that HPLC serves as a versatile technique which can be used for determination of majority of nutritional parameters that need to be mentioned on food nutrition labels.




Responses